In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, wind energy has emerged as a powerful contender. As we seek to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and combat climate change, harnessing the power of the wind presents an opportunity to transition toward a cleaner, more renewable energy future. Wind turbines are designed to convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy, making them a crucial component of modern energy production. This article will delve into the workings of wind energy, its advantages and challenges, different types of wind turbines, and the future potential of this renewable energy source.
What Is Wind Energy?

Wind energy refers to the process of capturing the energy produced by the wind and converting it into usable forms of energy, primarily electricity. Wind turbines, equipped with large blades, harness the wind’s force to spin a rotor connected to an electric generator. This process transforms kinetic energy into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy.
The Scale of Wind Energy
The United States, for instance, has a remarkable capacity for wind energy, generating nearly 10% of its electricity needs from this renewable source. As per the American Wind Energy Association (AWEA), the country boasts over 89 gigawatts (GW) of installed wind capacity, enough to power more than 28 million homes. This staggering figure illustrates the enormous potential of wind energy as a significant contributor to the national grid.
In contrast, countries like India are only beginning to invest in wind energy, with a current total installed capacity of around 42 GW. This difference highlights the varying stages of wind energy development across different regions, revealing the vast potential for growth in countries that are just starting to harness this resource.
How Do Wind Turbines Work?
This is a a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator.

Understanding how wind turbines operate is key to appreciating the efficiency and potential of wind energy. The blades of a wind turbine rotate when the wind blows, causing a rotor connected to a shaft to spin. This rotational movement drives an electric generator that produces electricity. The amount of electricity generated depends on two primary factors: the length of the turbine blades and the wind speed.
The Mechanics of Wind Turbines
When the wind hits the blades of the turbine, it creates lift, causing the blades to turn. This motion is transmitted to the rotor and then to the generator. The generator converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy, which is then transmitted to the power grid. The efficiency of this conversion process is essential for maximizing the output of wind energy systems.
The design and placement of wind turbines play a crucial role in their efficiency. Turbines are typically placed in open areas where wind flow is unobstructed, such as on hills, coastlines, and plains. By optimizing turbine placement, energy production can be maximized, contributing to the overall effectiveness of wind energy as a viable power source.
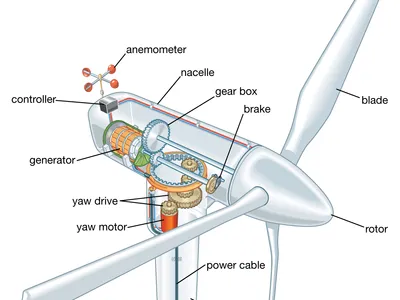
Types of Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are categorized into several types, primarily based on their design and axis of rotation. Here are the three main types:
- Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT):
- These are the most common type of wind turbines, characterized by blades that rotate around a horizontal axis. Typically mounted on tall towers, the height of the turbine significantly influences the amount of power generated. Higher installations allow turbines to capture stronger winds, resulting in more efficient electricity generation.
- Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT):
- Although less prevalent than HAWTs, vertical-axis turbines have blades that spin around a vertical axis. Their design allows them to capture wind from different directions, making them easier to maintain and more versatile in various wind conditions. This flexibility makes VAWTs a good choice for urban settings where wind direction may vary considerably.
- Downwind Turbines:
- Similar to horizontal-axis turbines, downwind turbines face the wind instead of being positioned upwind. This orientation allows them to harness strong winds more effectively and offers greater durability against wind pressure. Downwind turbines can also be beneficial in reducing the noise produced, making them a suitable option for residential areas.
Advantages of Wind Energy
Clean Energy Source
One of the primary benefits of wind energy is its status as a clean energy source. Unlike fossil fuels, wind energy does not produce harmful emissions or cause pollution. This characteristic is vital in combating climate change and reducing our carbon footprint. By transitioning to wind energy, we can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a healthier environment for future generations.
Renewable and Sustainable
Wind energy is a renewable resource, meaning it can be replenished naturally. As long as the sun shines and the earth rotates, there will be wind, making this form of energy sustainable for the long term. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and deplete over time, wind energy is consistently available, ensuring a continuous supply of electricity without the risk of depletion.
Cost-Effective
The cost of generating electricity from wind has fallen significantly over the past decade. As technology advances, wind energy has become one of the most cost-effective sources of electricity. This decline in cost encourages more investment in wind energy projects and promotes its widespread adoption. According to recent reports, the cost of onshore wind energy has dropped by more than 70% since 2009, making it competitive with traditional energy sources.
Economic Opportunities
Wind farms can create economic opportunities for local communities. They can provide an alternative source of income for farmers and rural communities, who may lease land for wind turbine installations. This practice can diversify income sources and stimulate local economies. Additionally, wind energy projects can create jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, further contributing to local economic growth.
Technological Innovations
Recent advancements in wind turbine technology have led to the development of larger, more efficient turbines. These innovations allow for greater energy capture and improved overall efficiency. For example, new materials and designs have enhanced the durability and performance of turbine blades, allowing them to operate effectively in a wider range of wind conditions.
Challenges in the Use of Wind Energy

Despite its numerous advantages, the use of wind energy is not without challenges. Understanding these challenges is essential for addressing potential concerns and enhancing the effectiveness of wind energy systems.
Intermittent Energy Source
One of the significant challenges of wind energy is its intermittent nature. Wind power generation can fluctuate due to varying wind speeds and directions, making it difficult to predict energy production accurately. This variability poses challenges for integrating wind power into existing electrical grids, which require stable and predictable power sources. To mitigate this issue, advancements in energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, are being explored to store excess energy produced during peak wind periods.
Upfront Costs
While the cost of generating wind energy has decreased, the initial investment required to build and install wind turbines remains high. This factor often necessitates government subsidies and incentives to make wind energy projects financially viable. Without such support, many projects may struggle to find funding. Policymakers play a crucial role in facilitating the growth of wind energy by providing necessary financial assistance and creating favorable regulatory frameworks.
Public Perception and Location Concerns
Public opposition to wind projects often stems from concerns about visual impact and potential noise pollution from wind turbines. As a result, developers tend to locate turbines far from densely populated areas, which can increase energy distribution costs. Balancing public perception and practical considerations is essential for successful wind energy projects. Engaging communities in the planning process and addressing their concerns can help foster support for wind energy initiatives.
Wildlife Impact
Another challenge associated with wind energy development is its potential impact on wildlife, particularly birds and bats. The construction and operation of wind farms can disrupt local ecosystems and pose risks to flying species. To minimize these impacts, developers are increasingly employing advanced siting techniques and technologies, such as radar systems, to monitor and mitigate risks to wildlife.
The Future of Wind Energy

Technological Advances
The future of wind energy looks promising, thanks in large part to ongoing technological advancements. Innovations in turbine design, such as larger and more efficient blades, have led to increased energy capture and improved overall efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more breakthroughs that will further enhance the viability of wind energy. Researchers are also exploring innovative solutions, such as floating wind farms that can be installed in deeper waters, expanding the potential for offshore wind energy generation.
Integration with Other Renewable Sources
Integrating wind energy with other renewable sources, such as solar power and hydroelectric systems, can create a more robust and reliable energy grid. This hybrid approach can help mitigate the challenges of intermittent energy production, ensuring a more stable power supply for communities. By combining different renewable technologies, we can optimize energy generation and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, paving the way for a cleaner energy future.
Global Growth and Investment
Globally, investment in wind energy is on the rise. Countries are recognizing the importance of diversifying their energy portfolios and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. As a result, the market for wind energy is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, with many nations striving to increase their installed wind capacity. According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), wind energy could become a leading source of electricity generation by 2050, contributing significantly to global energy needs.
Conclusion
Harnessing the power of the wind offers a transformative opportunity to address our energy needs sustainably. With numerous benefits, including its status as a clean and renewable energy source, wind energy has the potential to revolutionize the electricity generation sector. Despite the challenges associated with wind power, advancements in technology and growing public support pave the way for a brighter future.
As we strive for a sustainable energy landscape, investing in wind energy can help reduce our carbon footprint and contribute to a healthier planet. For those interested in further exploring this dynamic field
, Skill-Lync offers a range of courses on wind energy and related topics, providing valuable education and training for aspiring professionals.
Call to Action
Ready to dive deeper into the world of wind energy? Start your upskilling journey with Skill-Lync today and become part of the renewable energy revolution!







